Motherhood, Pregnancy
HOW OVERWEIGHT AFFECTS PREGNANCY?
Overweight can be defined as the high accumulation of fat on the body or high BMI (body mass index) than the optimal healthy BMI.
Being obese while pregnant can lead to complications for both you and your baby. The more overweight you are, the more likely you are to experience difficulties during your pregnancy. Hence it is very important being a pregnant woman to verify your weight as well as to take precautionary measures for the same.
Now let’s find out about obesity, its effect on your and on baby’s health, and how it can be maintained or reduced?

- How to measure if you are obese or not?
Obesity or overweight is considered when your BMI is 30 or greater than that. It can be calculated by dividing your weight by your height.
A high BMI can impact negatively your fertility by preventing proper ovulation. The greater the BMI, even in women who ovulate regularly, the longer it appears to take to become pregnant.
The female hormone estrogen is produced by your ovaries. Estrogen is produced by fat cells as well. Your fat cells expand and release more estrogen as you gain weight. Too much natural estrogen can make your body think you’re on estrogen-based birth control (such as the pill, injection, or vaginal ring) or that you’re already pregnant. This can make it difficult for you to ovulate and have monthly menstruation.
Extra weight may also lead to the failure of various fertility treatments from working like IVF (In-vitro fertilization), IVF is the process of combining an egg and sperm in a lab to make an embryo (fertilized egg) that is subsequently implanted into your uterus. The higher your BMI, the less likely you are to become pregnant with IVF.
You may also experience difficulties with testing, such as during ultrasounds. An ultrasound is a prenatal test that shows an image of your baby in the womb using sound waves and a computer screen.
RISK ASSOCIATED WITH OBESITY DURING PREGNANCY TO MOTHER’S HEALTH
- Gestational hypertension– High blood pressure during pregnancy in women (When the force of blood on the walls of blood arteries is too great, it is known as high blood pressure).
- Preeclampsia– If high blood pressure is not maintained during pregnancy, then gestational hypertension can lead to a dead serious condition called preeclampsia. Preeclampsia is a condition that can strike during or after the 20th week of pregnancy. It occurs when a pregnant woman has high blood pressure and evidence that her organs, such as her kidneys and liver, are malfunctioning.
- Clotting – Clotting is also one of the common risks associated with obesity during pregnancy where the blood clots partially or fully stop the flow of blood in a blood vessel.
- Gestational Diabetes– It is the diabetes that develops while a woman is pregnant. Obesity or being overweight increases the risk of gestational diabetes. Women who have experienced gestational diabetes are more likely to develop obesity and type 2 diabetes later in life. Low blood sugar in the newborn can be caused by gestational diabetes. Unborn babies may potentially be larger, putting the baby or the mother in danger during delivery.
- Repeated miscarriages and still births- When a baby dies in the womb before the 20th week of pregnancy, it is called a miscarriage. When a baby dies in the womb before birth but after 20 weeks of pregnancy, it is known as a stillbirth.
- Dysfunction of the heart
- Sleep deprivation– When your breathing stops while you’re sleeping, this is called sleep apnea.
- Venous thromboembolism is a hazardous blood clot condition (also called VTE). When a blood clot breaks off and travels through your bloodstream to organs such as the brain, lungs, or heart, this is known as thrombosis. A stroke or heart attack can occur as a result of this.
- The requirement for a C-section and the risk of complications from the procedure, such as wound infections.
RISK ASSOCIATED WITH OBESITY DURING PREGNANCY TO CHILD’S HEALTH –

If you are obese then the following complications can occur to the health of the child-
- Premature Birth– When the birth of an infant occurs before the 37th week of pregnancy then it is called as premature birth and it causes serious health risk and complications to the child’s health.
- Birth Defects– Neural tube defects (NTDs) and heart defects are two types of birth disorders. Birth malformations of the brain and spine are known as neural tube defects (NTDs). A birth defect is a health problem that a baby has at the time of birth. Birth defects alter the appearance or function of one or more body parts. They can have an impact on one’s overall health, how the body develops, and how the body functions. Even prenatal diagnostics like ultrasonography can make it difficult for your doctor to discover birth abnormalities during pregnancy.
- Macrosomia is a term used to describe a condition (also called large for gestational age or LGA). This signifies your baby was born weighing more than 8 kilos. A big baby might cause issues during labor and delivery, including harm to the baby. It also raises the likelihood of a c-section being required. Later in life, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, asthma, and obesity are common.
The baby can also develop issues like breathing problem, jaundice and low glucose level if you have gestational diabetes.
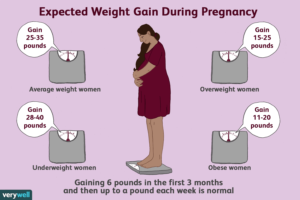
SPECIALIZED CARE DURING PREGNANCY–
If your BMI is 30 or more, your pregnancy will be constantly monitored by your doctor. He or she might suggest:
- Testing for gestational diabetes at an early stage. A glucose challenge test is commonly performed between weeks 24 and 28 of pregnancy for women at average risk of gestational diabetes. Your health care physician may offer the screening test at your first prenatal appointment if you have a BMI of 30 or higher. If your test results are normal, the screening test will most likely be repeated between weeks 24 and 28 of pregnancy. You’ll need more testing if the results are abnormal. Blood sugar monitoring and control can be discussed with your health care practitioner.
- Your foetal ultrasound has changed. A routine foetal ultrasound is performed between weeks 18 and 20 of pregnancy to assess the anatomy of the foetus. Ultrasound waves, on the other hand, have a hard time penetrating abdominal fat tissue. The effectiveness of prenatal ultrasonography may be impaired as a result of this. Consult your physician about the best method for obtaining a precise ultrasound.
- Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) screening. This is a potentially dangerous sleep disorder in which breathing stops and starts repeatedly throughout sleep. Preeclampsia and other problems are more likely in women who have obstructive sleep apnea during pregnancy. Your first prenatal checkup will most likely include a screening. Your health care physician may send you to a sleep medicine specialist for examination and treatment if obstructive sleep apnea is suspected.
STEPS TO BE TAKEN TO HAVE HEALTHY PREGNANCY
You can mitigate the negative effects of a high BMI on your health and the health of your kid by following measures-
- Make an appointment for a pre-conception exam. If you’re thinking about getting pregnant and have a BMI of 30 or higher, speak with your doctor. He or she may prescribe a daily prenatal vitamin and connect you to other health-care professionals, such as a qualified dietitian, who can assist you in achieving a healthy weight prior to conception.
- It is important to seek prenatal treatment on a regular basis. Prenatal visits can help your doctor keep track of your health and that of your baby. Any medical concerns you have, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnea, should be discussed with your health care provider, as well as what you can do to control them.
- Maintain a balanced diet. Maintain a balanced diet and avoid excessive weight gain by working with your health care practitioner or a trained dietitian. Keep in mind that you’ll require more folic acid, protein, calcium, iron, and other critical nutrients throughout pregnancy.
- Engage in some physical activity. Ask your doctor about safe methods to keep active while pregnant, such as walking, swimming, or practicing low-impact aerobics.
- Substances that are dangerous should be avoided. If you smoke, ask your doctor for assistance in quitting. Alcohol and illegal drugs are also prohibited. Before you start or stop using any medications or supplements, get your doctor’s approval.
This article has been written by Shivani Garg and the opinions expressed herein are the author’s own and do not reflect the view of 9HappyMonths. You can contact the author at shivanianugarg@gmail.com

